BVES Antibodies
Background
BVES gene encodes a transmembrane protein belonging to the spectrin superfamily, which is mainly expressed in vertebrate epithelial tissues and cardiac myocytes. This protein plays a key role in regulating epithelial barrier function and cardiomyocyte polarization by maintaining the integrity of intercellular junctions and participating in cell adhesion signal transduction. It was first identified in 1998 during the study of heart development. Subsequent research has found that abnormal expression of BVES protein is closely related to the metastasis of various cancers, inflammatory bowel disease, and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. The in-depth study of its structure and function provides an important molecular basis for understanding the maintenance of tissue barrier homeostasis and the mechanism of disease occurrence.
Structure of BVES
The BVES gene encodes a transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 42 kDa, belonging to the blood shadow protein superfamily. This protein exhibits highly conserved structural characteristics across different species, and its amino acid sequence homology exceeds 85% in humans, mice, and rats.
BVES protein consists of 316 amino acids and has three typical hydrophobic transmembrane domains. The extracellular segment contains glycosylation modification sites, and the intracellular segment has PDZ binding motifs, which are involved in cell signal transduction and assembly of junctional complexes. It is mainly expressed in epithelial tissues and cardiomyocytes, maintaining tissue barrier function by regulating intercellular junctions and polarity. The abnormal expression of this protein is closely related to tumor metastasis, inflammatory bowel disease and cardiovascular diseases.
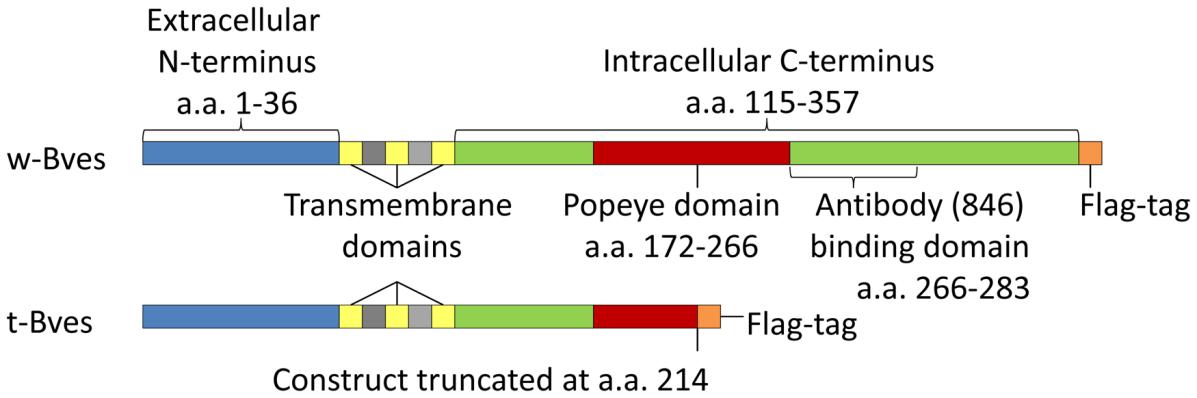 Fig. 1 Bves protein constructs.1
Fig. 1 Bves protein constructs.1
Key structural properties of BVES:
- Three transmembrane topology form hydrophobic core region
- Extracellular section contains conservative N - glycosylation modification site
- PDZ binding motif (ETSL motif) at the C-terminus of the cell
- N-terminal proline rich region is involved in protein interaction
Functions of BVES
The main function of the BVES gene is to maintain the integrity of the epithelial barrier and regulate cell adhesion. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of pathophysiological processes, including tumor suppression and cell polarity establishment.
| Function | Description |
| Barrier regulation | The BVES protein maintains the barrier function of epithelial tissues by strengthening the assembly of tight junctions and adhesive junctions, preventing pathogen invasion and tissue damage. |
| Regulation of cell adhesion | Regulate the adhesion force between epithelial cells and cardiomyocytes, and affect cell migration, spreading and tissue structure stability. |
| Tumor suppression | Lower the expression in a variety of cancer, inhibit epithelium, stroma (EMT) and transfer related pathways play a role of tumor suppressor. |
| Establishment of cell polarity | Participate in polarity protein the positioning and functions of regulation, plays an important role in tissue development and homeostasis to maintain. |
| Myocardial protection | Participate in ischemia-reperfusion injury in the heart of the response, regulating cell survival and energy metabolism signal process. |
BVES interacts with various signaling proteins (such as ZO-1 and MAGI-1) through its intracellular PDZ-binding motif, forming a regulatory network that coordinates functions such as cell connection, mechanical sensing, and gene expression.
Applications of BVES and BVES Antibody in Literature
1. Li, Haiwen, et al. "Defective BVES-mediated feedback control of cAMP in muscular dystrophy." Nature communications 14.1 (2023): 1785. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37496-8
The article indicates that BVES maintain skeletal muscle homeostasis by negatively regulating the ADCY9-cAMP-PKA signaling pathway. The absence of BVES enhances PKA activity, promotes FoxO-mediated protein degradation and autophagy, and leads to a decline in muscle mass and function. However, restoring BVES expression can reverse this process.
2. Shi, Yan, et al. "BVES downregulation in non-syndromic tetralogy of fallot is associated with ventricular outflow tract stenosis." Scientific Reports 10.1 (2020): 14167. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70806-4
Research has found that down-regulation of BVES expression is associated with right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) stenosis in non-syndromic tetralogy of Fallot (TOF). BVES affects the development of the cardiac outflow tract by positively regulating the transcriptional activity of key genes in the second heart area (SHF) such as GATA4, NKX2.5 and HAND2. Zebrafish experiments have confirmed that the absence of bves can lead to outflow tract stenosis and cardiac cycleization defects. This phenotype can be partially rescued by injecting bves mRNA or nkx2.5 mRNA.
3. Li, Haiwen, et al. "BVES is a novel interactor of ANO5 and regulates myoblast differentiation." Cell & Bioscience 11.1 (2021): 222. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-021-00735-w
This study discovered through proximity labeling technology that BVES is a novel interacting protein of ANO5. The two bind through the N/C terminal and co-localize on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Deletion of either ANO5 or BVES genes can significantly inhibit the differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts, indicating that the BVE-ANO5 complex plays a key role in regulating muscle differentiation.
4. Han, Ping, et al. "Cell adhesion molecule BVES functions as a suppressor of tumor cells extrusion in hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis." Cell Communication and Signaling 20.1 (2022): 149. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-022-00962-9
This study indicates that the down-regulation of BVES promotes the expulsion of liver cancer cells and aggravates tumor metastasis by regulating the distribution of ZO-1 and GEFT and enhancing the activity of RhoA. Overexpression of BVES can inhibit this process, providing a new target for the treatment of liver cancer.
5. Russ, Patricia K., et al. "Bves modulates tight junction associated signaling." PLoS One 6.1 (2011): e14563. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0014563
The article indicates that BVES affects the activities of RhoA and ZONAB/DbpA by regulating the formation of tight junctions (TJ). Full-length BVES enhance TJ function and promote membrane localization of ZO-1, ZONAB/DbpA and GEF-H1; However, the C-terminal truncated mutant disrupts its localization, resulting in a significant increase in RhoA activity and ZONAB/DbpA transcriptional activity.
Creative Biolabs: BVES Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality BVES antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom BVES Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our BVES antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Russ, Patricia K., et al. "Bves modulates tight junction associated signaling." PLoS One 6.1 (2011): e14563. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0014563
Anti-BVES antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






