Direct ELISA with Streptavidin-biotin Detection
For direct detection, the antigen or sample is coated directly on the multi-well plate and an enzyme-conjugated detection antibody binds to the solid antigen. Then, substrate is added, producing a signal which is proportional to the amount of antigen in the sample. Direct ELISA detection is much faster than other ELISA techniques because fewer steps are needed. The assay is also less prone to error because fewer reagents and steps are required.
As the antigen immobilization is not specific, higher background noise may be observed compared with indirect ELISA. This is primarily because all proteins in the sample, including the target protein, will bind to the plate. Direct ELISA is less flexible since a specific conjugated primary antibody is needed for each target protein. As no secondary antibody is used, there is no signal amplification, which reduces assay sensitivity. Click here for the Protocol of Direct ELISA with Streptavidin-biotin Detection.
Advantages
- Fast and simple protocol.
- Cross-reactivity of secondary antibody is eliminated.
Disadvantages
- Immunoreactivity of the primary antibody might be adversely affected by labeling with enzymes or tags.
- Labeling primary antibodies for each specific ELISA system is time-consuming and expensive.
- No flexibility in choice of primary antibody label from one experiment to another.
- No signal amplification- reduces assay sensitivity.
- Potential for high background.
When to use:
- Analyzing the immune response to an antigen.
- Assessing antibody affinity and specificity for an antigen.
- Investigating blocking or inhibitory interactions.
Direct ELISA vs Indirect ELISA
| Method | Pros | Cons |
| Direct | Quick methodology | Immunoreactivity of the primary antibody may be reduced as the result of labeling |
| Non-specific secondary antibody binding is eliminated | Little signal amplification | |
| Indirect | Sensitivity is increased | Non-specific binding may occur with the use of secondary antibody |
| Extra steps are required |
Optimization: Signal Amplification of Direct ELISA
For improved detection sensitivity, streptavidin-based amplification techniques are widely used. On the basis of direct ELISA, streptavidin-biotin detection provides signal amplification for medium- and low-abundance targets with a simple workflow. The affinity of streptavidin for biotin is the strongest non-covalent biological interaction known, with a dissociation constant (Kd) in the femtomolar range. Each streptavidin monomer can bind one biotin molecule, allowing a streptavidin protein to maximally bind four biotins with high affinity and selectivity.
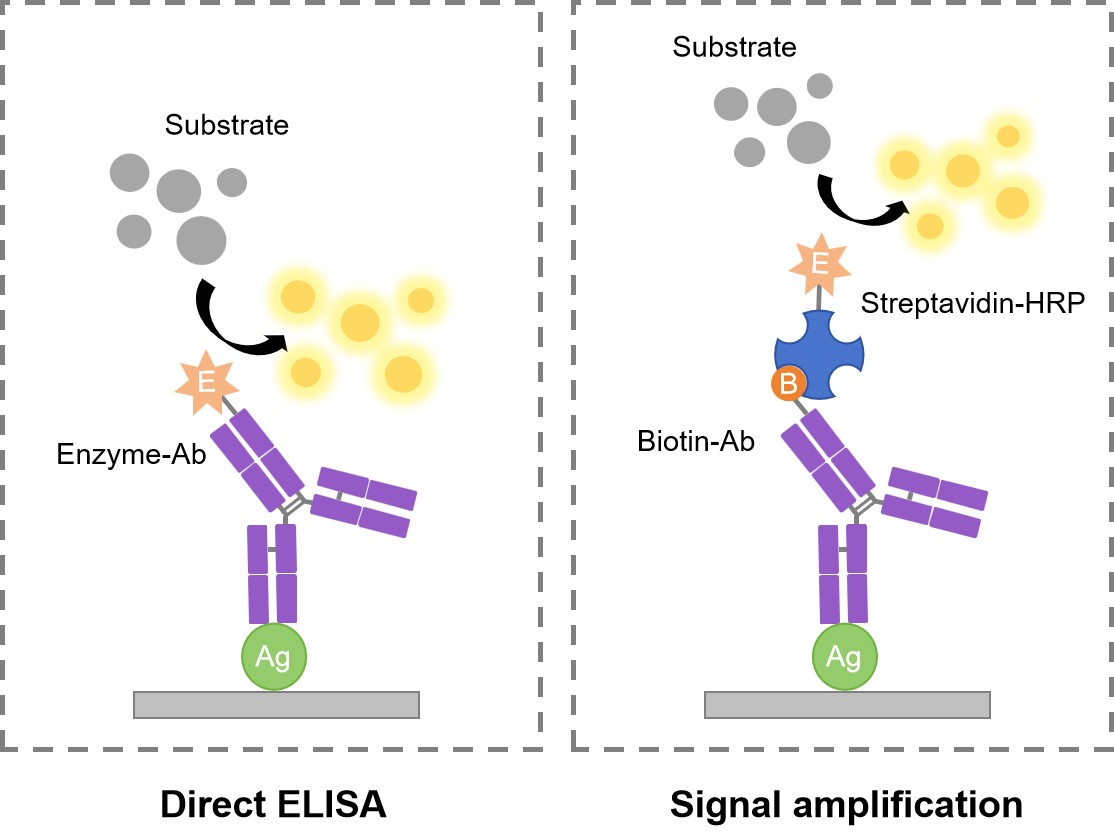 Fig.1 Normal mode and signal amplification mode of direct ELISA.
Fig.1 Normal mode and signal amplification mode of direct ELISA.
Advantages
- Highly specific.
- Rapid on-rate.
- Resistant to changes in pH or temperature.
- Withstand the presence of organic solvents and denaturing agents.
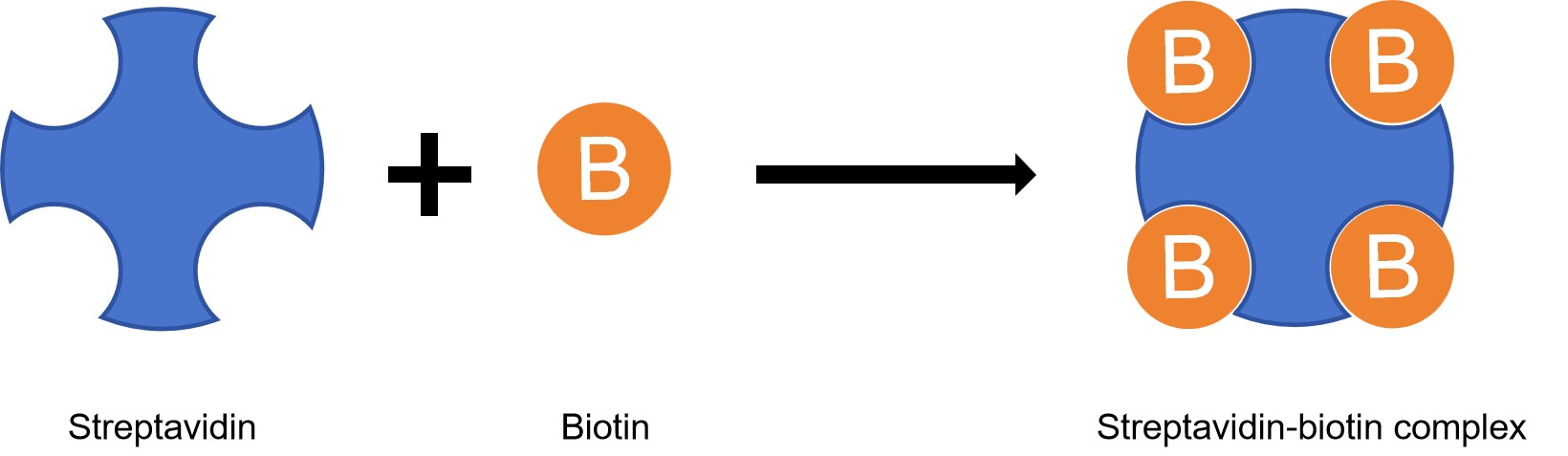
Streptavidin and biotin are used extensively in a wide range of laboratory applications. There are many ways in which their strong biological interaction can be exploited. Streptavidin conjugates are extremely popular in techniques such as Western Blot, ELISA and Flow Cytometry. By attaching the streptavidin protein to a moiety such as a fluorophore, an enzyme or a gold nanoparticle, the streptavidin-biotin interaction can be employed as a detection method. Our Troubleshooting of Direct ELISA with Streptavidin-biotin Detection is designed to help you improve and troubleshoot the common problems.
