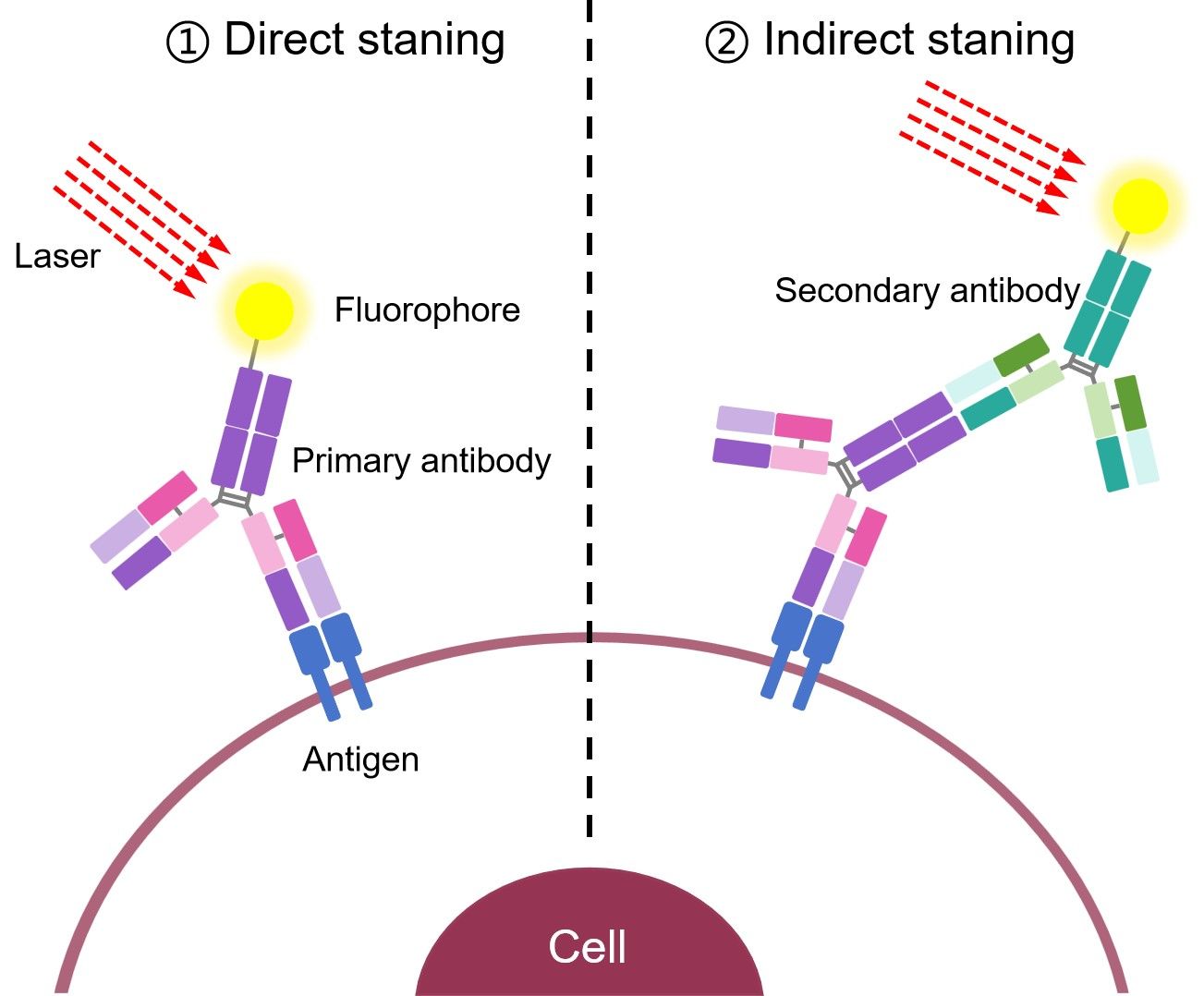
Indirect staining flow cytometry is essentially a kind of indirect immunoassay. In the indirect staining, the primary antibody is not labeled, and a secondary fluorochrome-labeled antibody with specificity for the primary antibody is used acting as the detection antibody. Alternatively, the streptavidin-biotin system could be used for signal amplification, whereby an antibody is conjugated to biotin and detected with fluorochrome-labeled streptavidin. With the availability of a wide range of conjugated antibodies at present, this method means that unconjugated primary antibodies raised against many different targets can be used in conjunction with a labeled secondary antibody for flow cytometric analysis. This broadens the choice of target proteins for the researcher.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Best for
If there is no available directly labeled antibody or you wish to amplify your signal, you can do indirect staining. This is where you stain a cell with a primary antibody against the antigen of interest and visualize using a labeled secondary antibody which recognizes the primary antibody.
Secondary Antibody Format for Flow Cytometry
The format of secondary antibody can impact the success of an experiment. Besides the whole molecule IgG, F(ab')2 fragments and Fc-specific F(ab) fragments could also be used as secondary antibody in flow cytometry assay.

F(ab')2 fragments are generated by proteolysis of the whole IgG to obtain a divalent fragment containing two F(ab) arms and no Fc domain. When used to stain cells and tissue, the F(ab')2 secondary antibodies can help to avoid background caused by off-target binding. The absence of Fc region prevents F(ab')2 antibodies from being captured by Fc receptors expressed on cell surfaces.
F(ab) anti-Fc fragment secondary antibodies are F(ab) fragment secondary antibodies specific to the Fc region of IgM or IgG primary antibodies. They could be conjugated with biotin and different fluorophores. Like F(ab')2 fragments, these F(ab) fragments can also minimize background staining due to Fc receptor binding.
Advantages of Using Fragment Secondary Antibodies in Flow Cytometry
Protocol of Indirect Staining Flow Cytometry and Troubleshooting of Indirect Staining Flow Cytometry are available for you. Please refer to the corresponding page for details.