TMPRSS2 Antibodies
Background
TMPRSS2 is a serine protease anchored to the cell membrane, mainly expressed in human tissues such as the prostate, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. The protein encoded by this gene can cleave and activate a variety of viral envelope proteins (including the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2) and cell signaling molecules, playing a key role in viral invasion of host cells and cell signaling. Its discovery can be traced back to the end of the 20th century and has become a research hotspot due to its close correlation with the mechanisms of various cancers (such as prostate cancer) and respiratory viral infections. The regulatory association between TMPRSS2 and androgen receptors is particularly prominent, which provides an important direction for targeted disease therapy. The research on its molecular mechanism continuously promotes the development of antiviral drugs and cancer treatment strategies.
Structure of TMPRSS2
The TMPRSS2 gene encodes a type II transmembrane serine protease with a molecular weight of approximately 54 kDa. This protein is composed of 492 amino acids, and its primary structure contains several key domains: a short cytoplasmic N-terminal, a transmembrane domain, a scavenger receptor-rich cysteine domain (SRCR), and an extracellular serine protease domain. Its catalytic active center is composed of a classic triad of histidine (His), aspartic acid (Asp), and serine (Ser), which is responsible for specifically cleaving the arginine or lysine residues of the substrate protein. The extracellular structure of this protein is stabilized by disulfide bonds and mediates interactions with cell surface receptors and viral proteins. The conformation of its protease domain directly determines the specificity of substrate recognition and catalytic efficiency.
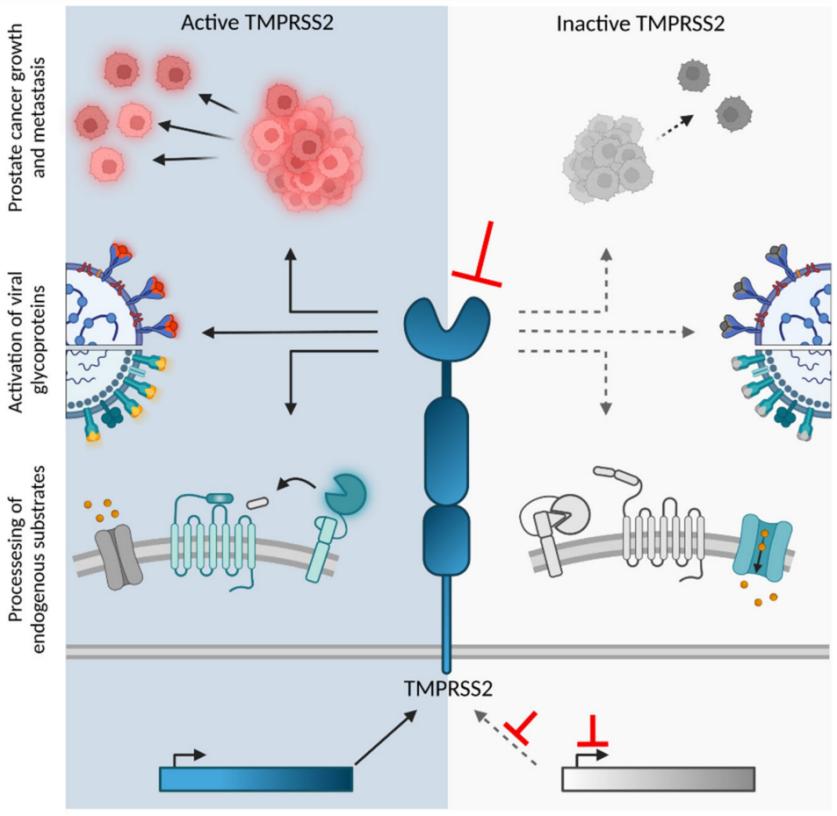 Fig. 1 (Patho)-physiological role of TMPRSS2.1
Fig. 1 (Patho)-physiological role of TMPRSS2.1
Functions of TMPRSS2
The primary function of TMPRSS2 is to mediate proteolytic cleavage on the cell surface, but its activity is also widely involved in various physiological and pathological processes such as viral infection, tumorigenesis, and cell signal transduction.
| Function | Description |
| Virus invasion promotion | Cut the spike proteins of various respiratory viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses), initiate membrane fusion and allow the viral genome to enter the host cell. |
| Occurrence of prostate cancer | Gene fusion with the ETS transcription factor family (especially ERG) has become a key molecular driving event for the occurrence of prostate cancer. |
| Cell signal activation | Hydrolyze and activate various cellular substrate proteins, such as protease-activated receptors (PARs), to participate in inflammatory and tissue repair responses. |
| Androgen regulation | Its expression is positively regulated by the androgen receptor (AR) signaling pathway and is significantly highly expressed in the foreglands and other androgen-sensitive tissues. |
| Maintenance of the epithelial barrier | Participation in epithelial cells maintain mucosal integrity, and by adjusting the ion channels and the effects of adhesion molecules connections between cells. |
The enzymatic activity of TMPRSS2 is typically substrate-specific, preferentially cleave the peptide bonds on the carboxyl side of arginine or lysine, and its optimal pH environment is slightly acidic. This characteristic is consistent with its highly efficient activation in the in vivo and cell surface microenvironment.
Applications of TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS2 Antibody in Literature
1. Pan, Zhengyang, Daoqun Li, and Leiliang Zhang. "TMPRSS2 in microbial interactions: Insights from HKU1 and TcsH." PLoS pathogens 20.11 (2024): e1012677. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1012677
The article indicates that TMPRSS2 is a key receptor that can bind to human coronavirus HKU1 and exotoxin TcsH, and its catalytic function is not essential in the interaction. This protein promotes viral membrane fusion through self-cleavage, and its structural mechanism provides a new target for the development of antiviral and anti-tumor drugs.
2. Wettstein, Lukas, Frank Kirchhoff, and Jan Münch. "The transmembrane protease TMPRSS2 as a therapeutic target for COVID-19 treatment." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.3 (2022): 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031351
The article indicates that TMPRSS2 is a transmembrane protease expressed in multiple tissues such as the respiratory tract, which can mediate the invasion process of various respiratory viruses such as SARS-CoV-2. The development of its inhibitors has become an important direction for antiviral treatment, especially having clinical potential for COVID-19.
3. Zipeto, Donato, et al. "ACE2/ADAM17/TMPRSS2 interplay may be the main risk factor for COVID-19." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 576745. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.576745
The article indicates that host proteins such as TMPRSS2 and ACE2 play a key role in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Its excessive activation may exacerbate inflammation and coagulation responses, especially in elderly men and patients with underlying diseases, and synergistically affect viral infection and the severity of the disease course in conjunction with ADAM17.
4. Keller, Christian, Eva Böttcher-Friebertshäuser, and Michael Lohoff. "TMPRSS2, a novel host-directed drug target against SARS-CoV-2." Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 7.1 (2022): 251. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01084-x
The article indicates that TMPRSS2 is a key protease for the novel coronavirus to invade host cells. Recent studies have shown that the small molecule inhibitor N-0385 can efficiently inhibit TMPRSS2 at nanomolmolar concentrations, block S protein cleavage, thereby preventing viral membrane fusion and infection, providing a new strategy for anti-COVID-19 treatment.
5. Gioukaki, Charitomeni, et al. "Unravelling the role of P300 and TMPRSS2 in prostate cancer: a literature review." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.14 (2023): 11299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411299
The article indicates that TMPRSS2 and its gene fusion with ERG are closely related to the occurrence and development of prostate cancer. Studies have shown that high expression of p300 is associated with malignant tumor progression. Inhibiting p300 can reduce the proliferation of cancer cells carrying TMPRSS2:ETS fusion. Combined targeted therapy may become a potential strategy.
Creative Biolabs: TMPRSS2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality TMPRSS2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom TMPRSS2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our TMPRSS2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Wettstein, Lukas, Frank Kirchhoff, and Jan Münch. "The transmembrane protease TMPRSS2 as a therapeutic target for COVID-19 treatment." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.3 (2022): 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031351
Anti-TMPRSS2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DLG1 Monolconal Antibody (4F3) (CBMAB-0225-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (61-3E7) (CBMAB-1183-CN)

-
Rat Anti-CD300A Recombinant Antibody (172224) (CBMAB-C0423-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








