Sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) are the most frequently used ELISA format. It requires the use of matched antibody pairs whereby each antibody is specific for different non-overlapping epitopes on the antigen. Firstly, one known as the capture antibody is coated onto the surface of a 96-well plate to facilitate the immobilization of the target antigen. Then the detection antibody binds to the capture antibody-antigen complex. Finally, an enzyme-labeled secondary antibody conjugates specific for the detection antibody is added. In direct sandwich ELISA format (shown in Fig.1, left), only two specific antibodies are used to sandwich the antigen. One is capture antibody and another is enzyme-labeled detection antibody. Either monoclonal or affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies can be used as capture and detection antibodies, depending on cost, the dynamic range and the sensitivity of the final assay.
Click here for the Protocol of Sandwich ELISA with Direct Detection and Troubleshooting of Sandwich ELISA with Direct Detection.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
| Best for: Analysis of complex samples, since the antigen does not need to be purified prior to measurement. | |
Different Forms of Sandwich ELISA
The procedure for a sandwich ELISA firstly requires the well of an ELISA plate to be coated with a capture antibody. The analyte or sample is then added, followed by the detection antibody. According to the detection principle and whether to use the enzyme-labeled capture antibody, sandwich ELISA could be divided into three forms, direct sandwich ELISA, indirect sandwich ELISA, and sandwich ELISA with streptavidin-biotin detection.
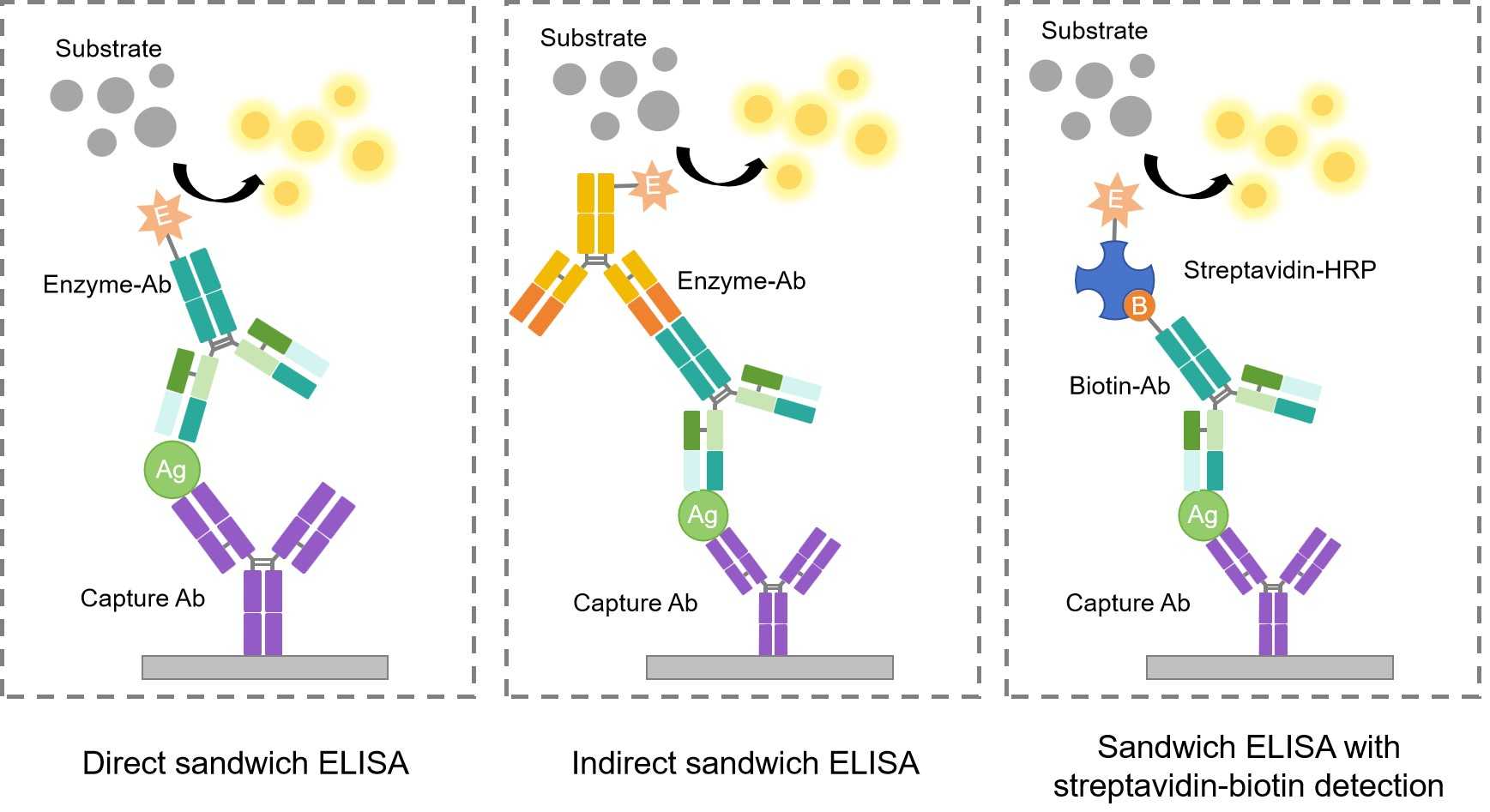 Fig.1 Different patterns of sandwich ELISA.
Fig.1 Different patterns of sandwich ELISA.
Streptavidin-biotin technology has been effectively used to improve ELISA detection due to the strong affinity between biotin and streptavidin because it has a dissociation constant (Kd) in the femtomolar range. Biotinylated probes are generally used to tag antibodies, antigens or peptides for subsequent detection using enzyme-conjugated streptavidin. Because biotin and streptavidin interact strongly, more analyte molecules can be captured on an ELISA plate.