Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTN4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-6075) (CBMAB-0020CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

Alzheimer's Disease Research
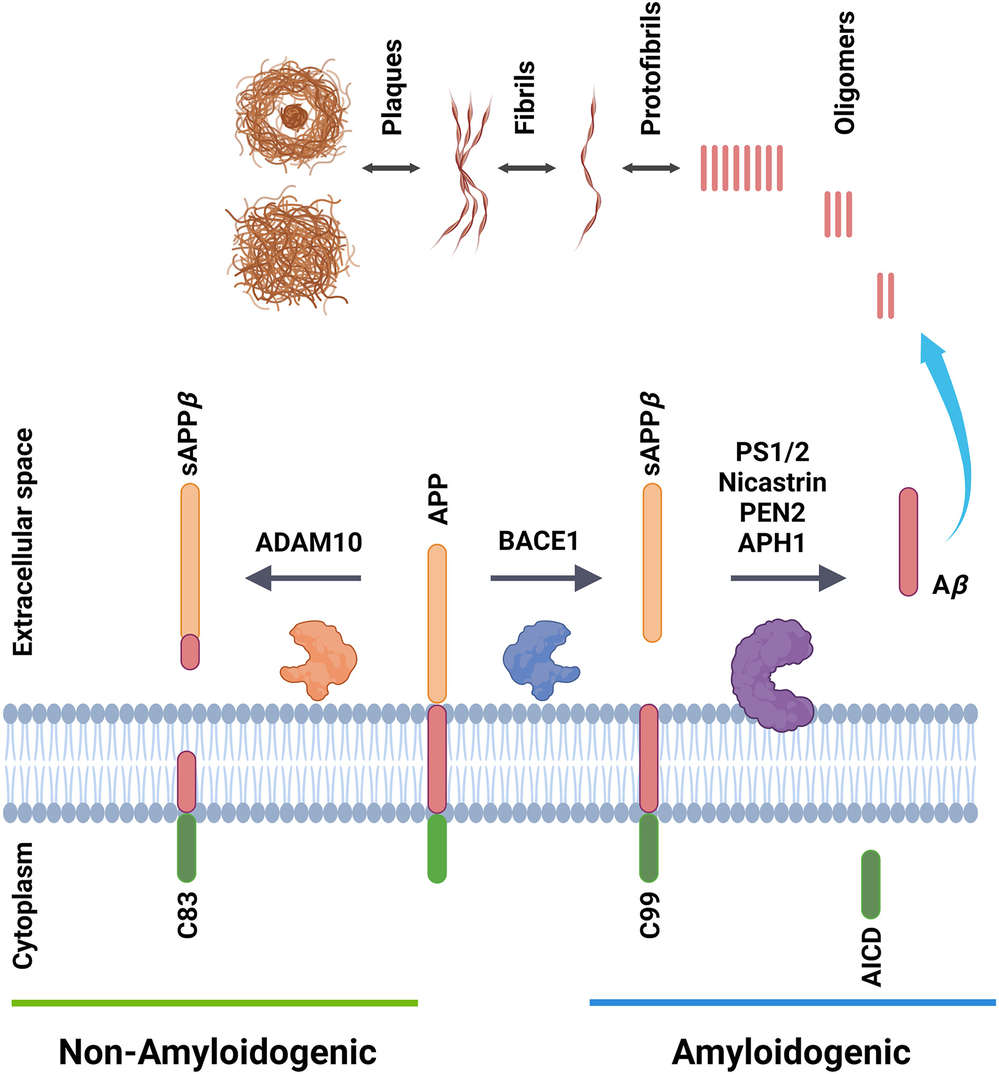
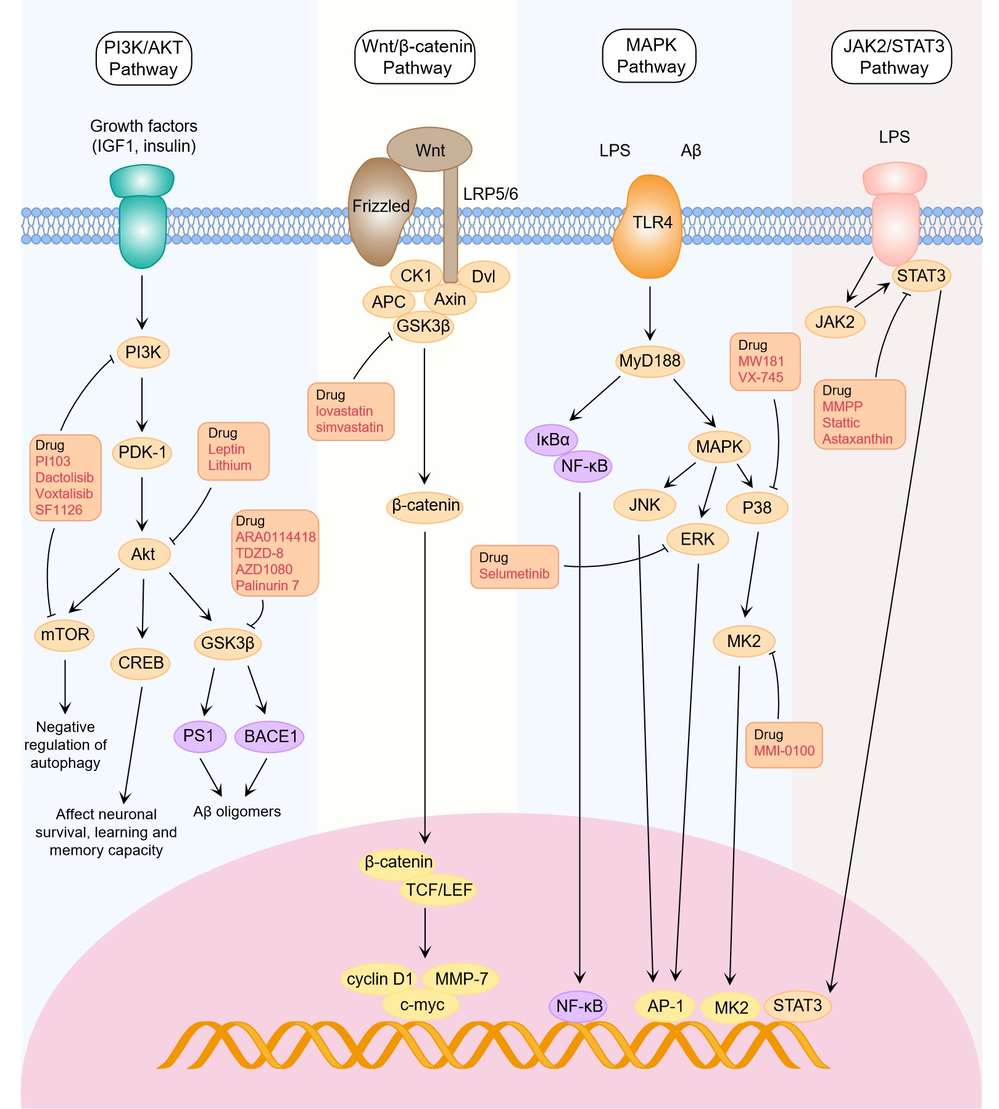
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that predominantly impacts older adults, making it the most common cause of dementia. It manifests as a constellation of impairments, including memory loss, cognitive decline, language difficulties, visuospatial dysfunction, and emotional disturbances. Genetic factors are believed to contribute to approximately 70% of AD risk, while other potential risk factors include head trauma, depression, and hypertension. AD is marked by distinct pathological features, including amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques aggregation and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) formation. These alterations severely disrupt neuronal function and contribute to neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction, ultimately leading to neuronal death. Current therapeutic strategies for AD are primarily focused on targeting these pathological features.
Learn more about our antibodies to support your AD diagnostic research and drug discovery, driving the development of innovative therapies for AD.
Please try the standard protocols which include: protocols, troubleshooting and guide.
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Flow Cytometry
Immunofluorescence (IF)
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Immunoprecipitation (IP)
Western Blot (WB)
Enzyme Linked Immunospot (ELISpot)
Proteogenomic
Other Protocols